


Climate change refers to a long-term shift in global or regional climate patterns. This shift can be caused by natural factors, such as changes in solar radiation or volcanic activity, but it is now primarily attributed to human activities, particularly the burning of fossil fuels (oil, coal, and gas) and deforestation....
The main driver of climate change is the increase of greenhouse gases in the Earth's atmosphere, particularly carbon dioxide. These gases trap heat from the sun and cause the planet to warm. As a result of this warming, the Earth's climate is changing in ways that have the potential to cause significant impacts on the planet and its inhabitants.
Some of the observed impacts of climate change include rising sea levels, more frequent and severe heatwaves, changes in precipitation patterns, increased frequency and intensity of extreme weather events such as hurricanes, droughts, and floods, and disruptions to ecosystems and biodiversity.
To mitigate and adapt to the impacts of climate change, it is important for individuals, businesses, and governments to take action. This can include reducing greenhouse gas emissions by transitioning to renewable energy sources, increasing energy efficiency, and promoting sustainable transportation and land use practices. Additionally, implementing climate adaptation measures, such as improving water management and building resilient infrastructure, can help to reduce the impacts of climate change on communities and ecosystems.
Clean and clever energy is critical for Pakistan's sustainable development and future prosperity. Here are some reasons why:...
Protection: The use of clean energy can significantly reduce the country's carbon footprint, helping to mitigate the effects of climate change and protect the environment. Pakistan has already been experiencing the adverse impacts of climate change, such as more frequent and severe heatwaves, droughts, and floods. By transitioning to clean energy, Pakistan can reduce its greenhouse gas emissions and improve air quality, leading to a healthier and cleaner environment for its citizens.
Economic Benefits: The shift to clean energy can also bring significant economic benefits to Pakistan. By investing in renewable energy, the country can create new job opportunities and reduce its dependence on imported fossil fuels. This can lead to cost savings for both the government and individuals, as well as increased energy security for the country.
Energy Access: Pakistan has a large population without access to reliable and affordable energy. Clean and clever energy can help to provide energy access to these communities, especially in rural and remote areas. Renewable energy sources such as solar, wind, and hydropower can provide a reliable and decentralized energy supply, reducing the country's dependence on centralized power grids.
Development: The transition to clean and clever energy aligns with the country's sustainable development goals, which aim to promote economic growth while protecting the environment and improving social welfare. By investing in clean energy, Pakistan can build a more sustainable and resilient economy that benefits all citizens.
In conclusion, the importance of clean and clever energy for Pakistan cannot be overstated. It is essential for the country's environmental protection, economic growth, energy access, and sustainable development. By taking action to transition to clean energy, Pakistan can ensure a brighter and more prosperous future for all its citizens.

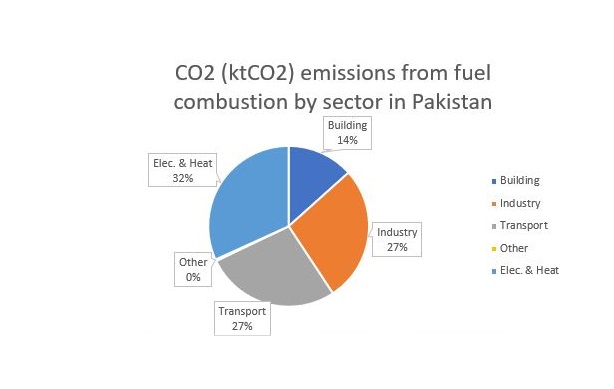
According to the International Energy Agency, the energy-related emissions in Pakistan in 2020 are mainly composed of the following:...
Electricity and Heat Production:The largest source of energy-related emissions in Pakistan is from electricity and heat production, accounting for about 32% of total energy-related emissions. This is due to the country's high reliance on fossil fuels for power generation, particularly on oil and natural gas.
Transportation:The transportation sector is the second-largest source of energy-related emissions in Pakistan, accounting for approximately 27% of total energy-related emissions. The growth of the transportation sector, coupled with the increasing use of fossil fuels, has contributed to this increase.
Industrial Processes:Industrial processes account for approximately 27% of energy-related emissions in Pakistan. The main contributors to industrial process emissions are the cement, fertilizer, and textile industries, which rely heavily on fossil fuels for their operations.
Residential and Commercial Buildings:Residential and commercial buildings account for approximately 14% of energy-related emissions in Pakistan. This is primarily due to the use of fossil fuels for heating and cooling, as well as for cooking and lighting in households and commercial buildings.
Other Energy-Related Activities:Other energy-related activities, such as agriculture and fishing, account for the remaining 0% (542 KtCO2) of energy-related emissions in Pakistan.
Overall, the majority of energy-related emissions in Pakistan come from the electricity and heat production sector, followed by transportation, industrial processes, and residential and commercial buildings. Addressing these sectors is critical to reducing the country's greenhouse gas emissions and combating climate change.
Pakistan has significant potential to reduce its greenhouse gas emissions from the energy sector through a variety of measures. Some of the key strategies to reduce emissions from energy in Pakistan include:...
Expanding Renewable Energy: Pakistan has abundant renewable energy resources, including solar, wind, and hydropower. The country has set a target of generating 30% of its electricity from renewable sources by 2030. Increasing the share of renewable energy in the country's electricity mix would reduce emissions from the power sector, while also improving energy security and creating new job opportunities.
Improving Energy Efficiency:Energy efficiency measures can help to reduce the amount of energy needed to power homes, businesses, and industries. This can be achieved through measures such as upgrading building insulation, improving lighting efficiency, and using more efficient industrial equipment. Such measures can help reduce energy consumption and associated greenhouse gas emissions.
Enhancing Energy Conservation:Energy conservation is another important strategy to reduce emissions from the energy sector. This can involve measures such as promoting public transportation, reducing wasteful energy practices, and encouraging the adoption of energy-efficient technologies.
Reducing Fossil Fuel Use:Pakistan relies heavily on fossil fuels, particularly oil and natural gas, for power generation. Reducing the use of these fuels and shifting to cleaner alternatives such as renewables can significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
Promoting Carbon Capture and Storage:Carbon capture and storage (CCS) technology can capture carbon dioxide emissions from power plants and other industrial sources and store them underground. Promoting the adoption of CCS technology can help reduce emissions from the energy sector.
Strengthening Policy and Regulatory Frameworks: Strong policy and regulatory frameworks can play a critical role in promoting low-carbon energy and reducing emissions from the energy sector. This can involve measures such as carbon pricing, renewable energy standards, and energy efficiency regulations.
In summary, reducing emissions from energy is critical for Pakistan to address the challenge of climate change. Adopting a mix of renewable energy, energy efficiency, energy conservation, and other low-carbon technologies, along with a supportive policy and regulatory framework, can help to achieve this goal.
Renewable Energy in Pakistan:Opportunities and Benefits for a Sustainable Energy Future Renewable energy is a key opportunity for many countries, including Pakistan, for a number of reasons:
Energy Security:Renewable energy sources like wind, solar, and hydro are domestic resources that can help reduce a country's dependence on imported fossil fuels, increasing energy security and reducing vulnerability to global energy price shocks.
Environmental Sustainability:Renewable energy sources emit little to no greenhouse gases, which contribute to climate change and air pollution. By transitioning to renewable energy sources, countries like Pakistan can improve air quality, reduce carbon emissions, and mitigate the impact of climate change.
Economic Development:The renewable energy sector has the potential to create new jobs and stimulate economic growth. For example, the development of wind and solar power projects requires skilled labor and can create new opportunities for businesses and entrepreneurs.
Cost-Competitive:Renewable energy technologies, particularly solar and wind power, have become increasingly cost-competitive with traditional fossil fuel sources. This has made them an attractive option for countries looking to diversify their energy mix and reduce their reliance on fossil fuels.
Scalability:Renewable energy sources can be deployed at a variety of scales, from small-scale residential solar panels to large-scale wind farms and hydropower plants. This flexibility allows countries to tailor their energy systems to their specific needs and resources.
In Pakistan specifically, renewable energy is a key opportunity for the country to address its energy challenges, including energy insecurity, environmental degradation, and economic development. By investing in renewable energy technologies and expanding their use, Pakistan can move towards a more sustainable and secure energy future.


Pakistan has made several climate change commitments, including its Nationally Determined Contribution (NDC) to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) and the Paris Agreement. These commitments include:...
Reduction of Greenhouse Gas Emissions:Pakistan has committed to reducing its greenhouse gas emissions by 20% by 2030, with a further reduction of 10% conditional upon international support.
Increased Use of Renewable Energy:Pakistan aims to increase the share of renewable energy in its total power generation to 30% by 2030. This includes targets for the development of solar, wind, and hydropower projects.
Implementation of Energy Efficiency Measures:Pakistan has committed to implementing energy efficiency measures in the industrial, transport, and agriculture sectors, with a goal of reducing energy consumption by 10% by 2030.
Reforestation and Forest Conservation:Pakistan has set a goal of planting 10 billion trees by 2023 as part of its efforts to increase forest cover and reduce carbon emissions.
Climate Resilience:Pakistan has committed to enhancing its resilience to the impacts of climate change, including through the development of early warning systems for extreme weather events, the implementation of adaptation measures in vulnerable communities, and the integration of climate change considerations into national planning and decision-making.
These commitments reflect Pakistan's recognition of the urgent need to address the global challenge of climate change and the country's willingness to take action to mitigate its own contribution to the problem. While the success of these commitments will depend on effective implementation and ongoing support from the international community, they represent an important step towards a more sustainable and resilient future for Pakistan and the world.